Favorite Define Double Displacement

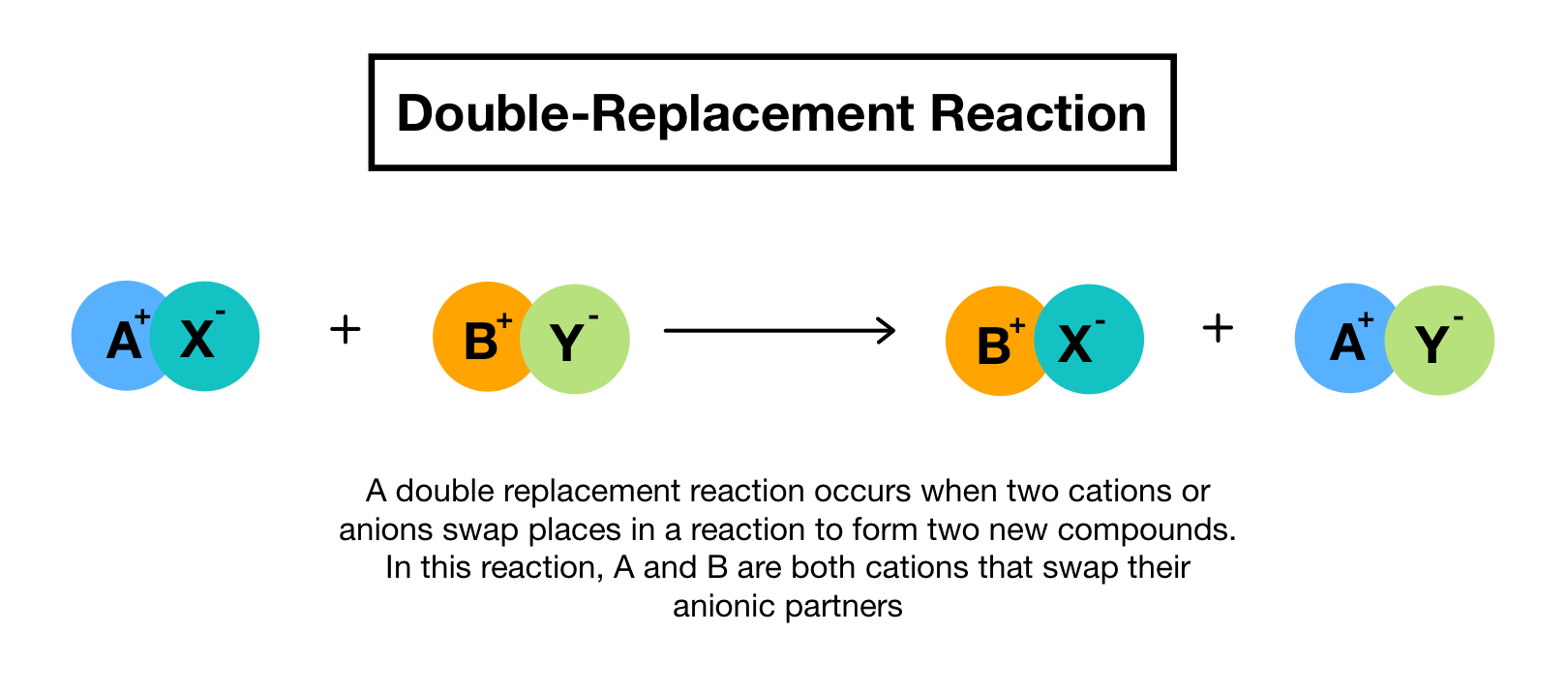
A double displacement reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the exchange of two ionic species between two different molecules.
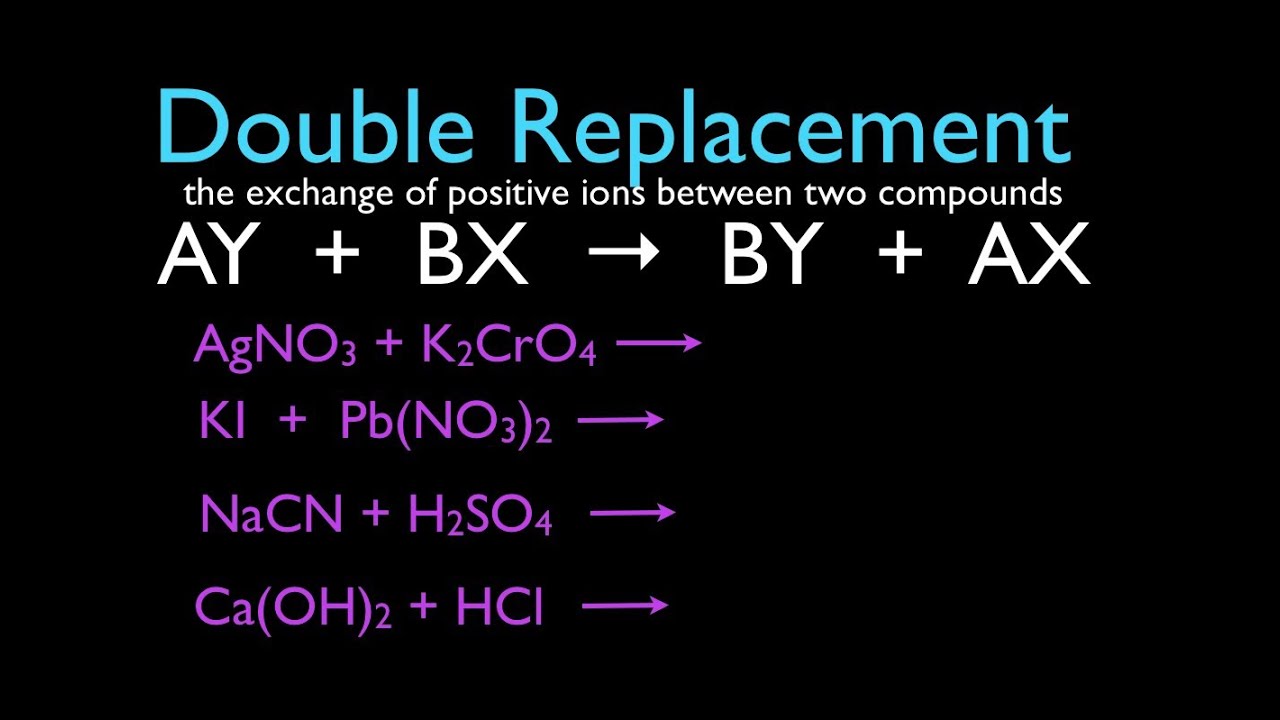
Define double displacement. Single displacement reactions are reactions where one reactant replaces part of the other. A double replacement reaction is a type of chemical reaction that occurs when two reactants exchange cations or anions to yield two new products. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high.
Double displacement reactions are those reactions where the cations and anions of reactants switch places with each other or replaces each other. This ScienceStruck post explains the concept of double displacement reaction in chemistry along with a few examples. Usually a double displacement reaction results in precipitate formation.
The chemical bonds between the reactants may be either covalent or ionic. A chemical reaction between two compounds in which the first and second parts of one reactant are united respectively with the second and first parts. Here both iron and copper have the same valence.
Usually a double displacement reaction results in precipitate formation. A double displacement reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which the reactant ions exchange places to form new products. Double displacement reactions may be defined as the chemical reactions in which one component each of both the reacting molecules is exchanged to form the products.
One metal cation takes the place of the other bonding to the. Double Replacement Reaction Calculator. A double displacement reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which the reactant ions exchange places to form new products.
Double displacement synonyms double displacement pronunciation double displacement translation English dictionary definition of double displacement. A double displacement reaction is an important type of chemical reaction to know when studying chemistry. Double-displacement meaning A chemical reaction between two compounds in which the first and second parts of one reactant are united respectively with the second and first parts of the other reactant.