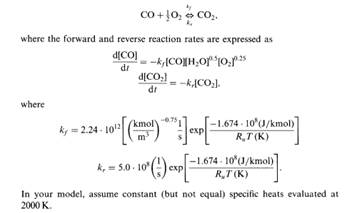Neat Co Combustion Reaction

The objec-tives of the present study are 1 to provide an up-date for the H 2CO combustion reaction model on the basis of recent kinetic data and 2 to opti-mize the H CO model against available H CO combustion data.
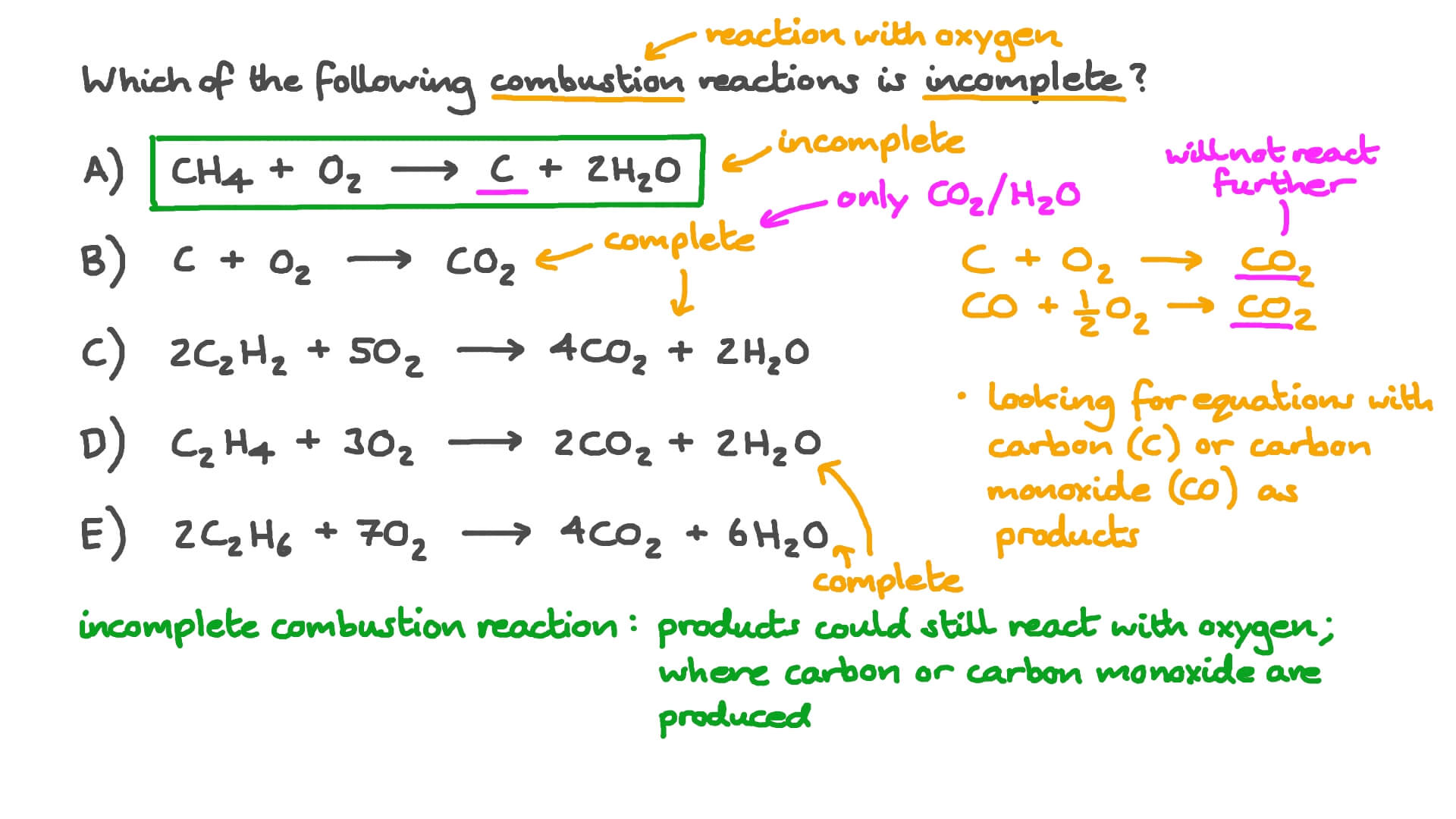
Co combustion reaction. A combustion reaction is when a substance reacts with oxygen and releases a huge amount of energy in the form of light and heat. This is mostly thermal energy but. The calorific value is the total energy released as heat when a substance undergoes complete combustion with oxygen under standard conditions.
The general form of a combustion reaction can be represented by the reaction between a hydrocarbon and oxygen which yields carbon dioxide and water. It may be expressed with the quantities. Combustion is an exothermic reaction in that it involves the release of energy in the form of light and heat.
Carbon dioxide - CO2 - is a combustion product and the content of CO2 in a flue gas is an important indication of the combustion efficiency. High-Temperature Combustion Reaction Model of H2COC1-C4 Compounds. Combustion reactions must involve O 2 as one reactant.
A combustion reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which a compound and an oxidant are reacted to produce heat and a new product. Catalytic combustion is a promising technology to improve combustion efficiency and reduce environmental pollutions. During complete combustion carbon and hydrogen combine with oxygen O2 to produce carbon dioxide CO2 and water H2O.
Collects carbon C as carbon dioxide CO2 and collects hydrogen H as water H2O. Optimal content of carbon dioxide CO2 after combustion is approximately 10 for natural gas and approximately 13 for lighter oils. Combustion reactions Combustion is another name for burning.
A combustion reaction is a major class of chemical reactions commonly referred to as burning In the most general sense combustion involves a reaction between any combustible material and an oxidizer to form an oxidized product. The combustion of hydrogen gas produces water vapor. The reaction of the co-combusted coal and waste was more intense and the thermal profile shows the co-combusted fuel with a higher peak temperature and a lower burnout temperature compared to lignite alone 15.