Great Equation Of Reaction

This equation is sometimes written as ratefrac.
Equation of reaction. The Arrhenius equation gives the dependence of the rate constant of a chemical reaction on the absolute temperature as where k is the rate constant frequency of collisions resulting in a reaction T is the absolute temperature in kelvins A is the pre-exponential factor a constant for each chemical reaction E a is the activation energy for the reaction in the same units as RT. In this equation H2. The rate constant k for the reaction or enough information to determine it.
To balance a chemical equation enter an equation of a chemical reaction and press the Balance button. Chemical equations are representations of chemical reactions in terms of symbols of elements and formulas of compounds involved in the reactions. Use uppercase for the first character in the element and lowercase for the second character.
In these equations s stands for solid l for liquid l and g for gas. An example of a chemical equation. The order of the reaction or enough information to determine it.
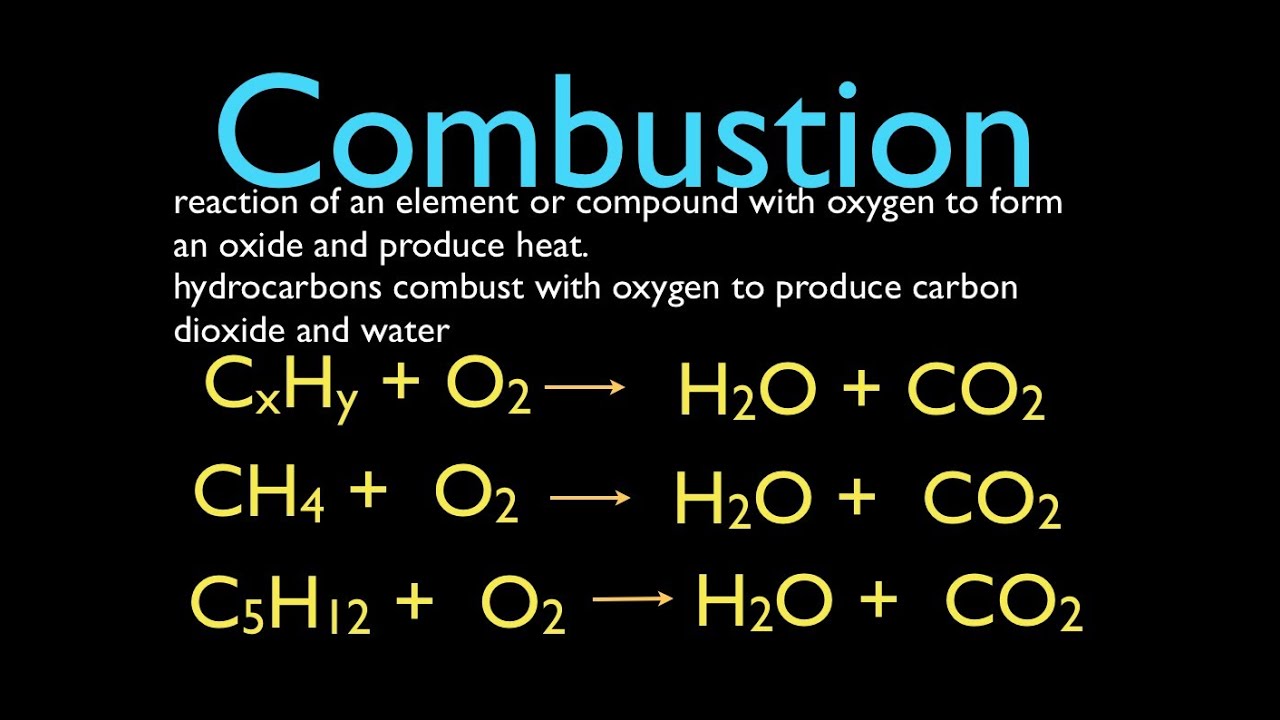
The heat or enthalpy of a chemical reaction is the difference between the heats of formation of products. The substances that enter into a chemical reaction are called reactants and the substances formed are the products. To find H for a reaction first identify its products and reactants.
The skeleton equation for the reaction on which this titration is based can be written as follows. Assign oxidation numbers to atoms on both sides of the equation. Equations Inequalities Simultaneous Equations System of Inequalities Polynomials Rationales Coordinate Geometry Complex Numbers PolarCartesian Functions Arithmetic Comp.
For example melting sublimation evaporation and condensation can be represented as follows. Give the equations of reactions for the preparation of phenol from cumene. These two equations are described as electron-half-equations half-equations or ionic-half-equations or half-reactions Every redox reaction is made up of two half-reactions.